What is the difference between rheumatoid diseases and each other? How to detect the problem in time?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic inflammatory disease of the connective tissue, in which the patient affects small joints (elbows, knees, hands and feet) of the erosive-destructive type. The result is bone erosion and its subsequent deformation. Over time, the symptoms of the disease worsen and lead to disability. About 60 million people in the world suffer from this disease. The disease affects women more often, whose average age is 30 to 35 years.
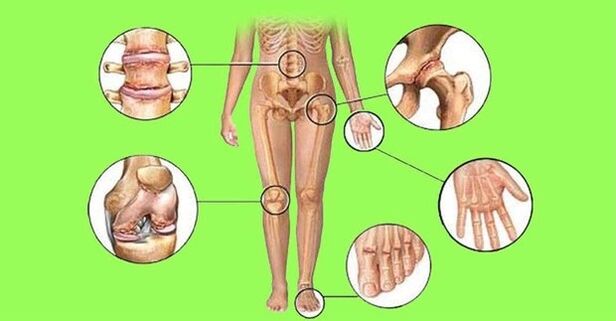
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease that affects the cartilaginous tissues of the ankle, knee, shoulder, hip and foot joints. The progressive form turns into osteoarthritis, which creates limitations in a person's motor activity. The disease can develop in two symmetrical joints at once. Sometimes in different ones, for example, the knee and the hip on the same limb.
Rheumatoid polyarthritis is a current problem of modern rheumatology. Apart from the joints, the disease also spreads to the internal organs and muscles. The disease develops symmetrically on both arms or legs. The disease often leads to disability.
Rheumatism affects the connective tissue of the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal system, knee joints, elbows, ankle joints and the heart itself. Locally, the disease can affect a person's internal organs and systems. The disease requires timely treatment. Failure to do so will result in fatal complications.
The main differences
Sick people come to the doctor with complaints of joint discomfort, pain and limited mobility. The symptoms of arthritis and arthrosis are similar, but there are characteristic differences.
arthritis changes:
- synovial membrane with fluid, joint capsule becomes inflamed;
- heat;
- redness in the painful area;
- two joints hurt at the same time;
- no joint deformity.
Cartilage inflammation begins with an infection, injury, or disturbance in the metabolic process.
Physiology of arthrosis:
- modified compound;
- cartilage tissue worn away with age;
- inflammation, swelling and redness are not observed;
- normal temperature;
- only one joint is affected.
Diseases bring suffering to a person when he performs simple actions: bending, bending, straightening, lifting his legs or arms. The patient can barely sit on the chair, he goes down the stairs.
Signs and symptoms
Diseases have common symptoms:
- difficulty walking;
- the presence of pain in the inflamed area;
- poor mobility of the problem area.
The usual way of life of a sick person is disrupted. Every morning, getting out of bed, you need to "break up" to go to the kitchen, overcoming the pain.
What is more dangerous
Diseases bring a lot of pain and trouble to the patient.
Arthritis is caused by inflammation in the body. He is being treated. It is important to contact a specialist in time, and not wait for bone erosion and other complications.
Arthrosis is a "disease of the elderly" with changes within the joint. The worn cartilage thins out. Synovial fluid, which is the source of tissue nutrition, is not renewed. The consequences of the disease are irreversible. To alleviate the person's condition, there can be a specialist who will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics
It consists of carrying out various procedures and activities. During the examination, the doctor learns from the patient with arthritis information about previous infections and injuries. Determines the course of the disease and prescribes diagnostics:
- A blood test to detect uric acid.
- Ultrasound of joints.
- X-ray of the affected area.
- CT.
- Arthroscopy.
The results show the clinical picture of the disease in full.
Diagnosis of arthrosis step by step:
- Visually, the doctor assesses the mobility of the joint. Whether or not there are ossified areas in the problem area, whether a crunch is heard. What is the condition of the muscles around the painful joint?
- Bony growths and deformity of the joint help to see the X-ray.
- Synovial fluid analysis and histology.
- Complete blood count.
Physical training
I would like to mention that exercise therapy, swimming - effectively help in the prevention and treatment of arthrosis. Physical activity is aimed at restoring joint mobility. By increasing the blood flow in the affected area, cleaning and restoration of the joint tissue is encouraged.
We must not forget about the limitations of physiotherapy exercises:
- It is performed in the period of remission in the absence of severe pain.
- In old age, existing piles of diseases or serious joint degradation do not allow engaging in physical exercises.
- Overweight patients are allowed to do a limited amount of exercise without serious strain.
- The effect of exercise therapy is regular exercise alternating with rest periods for the joint.
Rheumatoid diseases are treated by rheumatologists and orthopedic traumatologists. Early diagnosis and proper treatment will allow you to live without complications. A patient who seeks help in time will have the opportunity to continue to exist normally. In arthrosis, this is the relief of the condition, stopping the progression of the disease. And most importantly, don't become disabled.


























